
Decrypt and crack your MD5, SHA1, SHA256, MySQL, and NTLM hashes for free online. We also support Bcrypt, SHA512, Wordpress and many more. PDF 1.1-1.7 password recovery available for online orders Altcoin payments accepted here! We now accepting Litecoin (LTC), DASH and Zcash (ZEC) payments. New tasks will have Bitcoin (BTC) payment bound by default but you can manually change it to other.
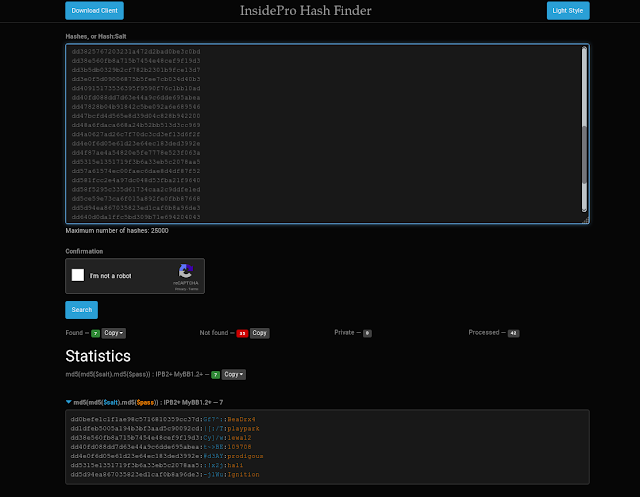
Hashes.com is a hash lookup service. This allows you to input an MD5, SHA-1, Vbulletin, Invision Power Board, MyBB, Bcrypt, Wordpress, SHA-256, SHA-512, MYSQL5 etc hash and search for its corresponding plaintext ('found') in our database of already-cracked hashes.
It's like having your own massive hash-cracking cluster - but with immediate results!
We have been building our hash database since August 2007.
We are not cracking your hash in realtime - we're just caching the hard work of many cracking enthusiasts over the years.
The MD5 message-digest algorithm is a widely used hash function producing a 128-bit hash value. Although MD5 was initially designed to be used as a cryptographic hash function, it has been found to suffer from extensive vulnerabilities. It can still be used as a checksum to verify data integrity, but only against unintentional corruption. It remains suitable for other non-cryptographic purposes, for example for determining the partition for a particular key in a partitioned database. The weaknesses of MD5 have been exploited in the field, most infamously by the Flame malware in 2012. The CMU Software Engineering Institute considers MD5 essentially cryptographically broken and unsuitable for further use. MD5 Decrypt.

In cryptography, SHA-1 (Secure Hash Algorithm 1) is a cryptographic hash function which takes an input and produces a 160-bit (20-byte) hash value known as a message digest – typically rendered as a hexadecimal number, 40 digits long. It was designed by the United States National Security Agency, and is a U.S. Federal Information Processing Standard. Since 2005 SHA-1 has not been considered secure against well-funded opponents, and since 2010 many organizations have recommended its replacement by SHA-2 or SHA-3. Microsoft, Google, Apple and Mozilla have all announced that their respective browsers will stop accepting SHA-1 SSL certificates by 2017. SHA1 Decrypt.
The MySQL5 hashing algorithm implements a double binary SHA-1 hashing algorithm on a users password. MySQL Decrypt.
NT (New Technology) LAN Manager (NTLM) is a suite of Microsoft security protocols that provides authentication, integrity, and confidentiality to users. NTLM is the successor to the authentication protocol in Microsoft LAN Manager (LANMAN), an older Microsoft product. The NTLM protocol suite is implemented in a Security Support Provider, which combines the LAN Manager authentication protocol, NTLMv1, NTLMv2 and NTLM2 Session protocols in a single package. Whether these protocols are used or can be used on a system is governed by Group Policy settings, for which different versions of Windows have different default settings. NTLM passwords are considered weak because they can be brute-forced very easily with modern hardware. NTLM Decrypt.
See Full List On Cracker.offensive-security.com
SHA-2 (Secure Hash Algorithm 2) is a set of cryptographic hash functions designed by the United States National Security Agency (NSA). They are built using the Merkle–Damgård structure, from a one-way compression function itself built using the Davies–Meyer structure from a (classified) specialized block cipher. SHA-2 includes significant changes from its predecessor, SHA-1. The SHA-2 family consists of six hash functions with digests (hash values) that are 224, 256, 384 or 512 bits: SHA-224, SHA-256, SHA-384, SHA-512, SHA-512/224, SHA-512/256. Sm-j400m firmware. SHA256 Decrypt.
The Preempt research team found two critical Microsoft vulnerabilities that consist of three logical flaws in NTLM, the company's proprietary authentication protocol.
These vulnerabilities allow attackers to remotely execute malicious code on any Windows machine or authenticate to any web server that supports Windows Integrated Authentication (WIA) such as Exchange or ADFS.
The research shows that all Windows versions are vulnerable.
The flaws allow attackers to bypass existing mitigations
NTLM is susceptible to relay attacks, which allows actors to capture an authentication and relay it to another server, granting them the ability to perform operations on the remote server using the authenticated user's privileges. NTLM Relay is one of the most common attack techniques used in Active Directory environments, where the attacker compromises one machine, then moves laterally to other machines by using NTLM authentication directed at the compromised server.
Microsoft previously developed several mitigations for preventing NTLM relay attacks, but Preempt researchers discovered those mitigations have the following exploitable flaws:
The Message Integrity Code (MIC) field ensures that attackers do not tamper NTLM messages. The bypass discovered by Preempt researchers allows attackers to remove the ‘MIC' protection and modify various fields in the NTLM authentication flow, such as signing negotiation.
SMB Session Signing prevents attackers from relaying NTLM authentication messages to establish SMB and DCE/RPC sessions. The bypass enables attackers to relay NTLM authentication requests to any server in the domain, including domain controllers, while establishing a signed session to perform remote code execution. If the relayed authentication is of a privileged user, this means full domain compromise.
Enhanced Protection for Authentication (EPA) prevents attackers from relaying NTLM messages to TLS sessions. The bypass allows attackers to modify NTLM messages to generate legitimate channel binding information. This allows attackers to connect to various web servers using the attacked user's privileges and perform operations such as: read the user's emails (by relaying to OWA servers) or even connect to cloud resources (by relaying to ADFS servers).
'Even though NTLM Relay is an old technique, enterprises cannot completely eliminate the use of the protocol as it will break many applications. Hence it still poses a significant risk to enterprises, especially with new vulnerabilities discovered constantly,' stated Roman Blachman, CTO, Preempt. 'Companies need to first and foremost ensure all of their Windows systems are patched and securely configured. In addition, organizations can further protect their environments by gaining network NTLM visibility. Preempt works with its customers to ensure they have this visibility and the best protection possible.'
Protection strategies
In order to protect themselves from these vulnerabilities, organizations must:
Decrypt and crack your MD5, SHA1, SHA256, MySQL, and NTLM hashes for free online. We also support Bcrypt, SHA512, Wordpress and many more. PDF 1.1-1.7 password recovery available for online orders Altcoin payments accepted here! We now accepting Litecoin (LTC), DASH and Zcash (ZEC) payments. New tasks will have Bitcoin (BTC) payment bound by default but you can manually change it to other.
Hashes.com is a hash lookup service. This allows you to input an MD5, SHA-1, Vbulletin, Invision Power Board, MyBB, Bcrypt, Wordpress, SHA-256, SHA-512, MYSQL5 etc hash and search for its corresponding plaintext ('found') in our database of already-cracked hashes.
It's like having your own massive hash-cracking cluster - but with immediate results!
We have been building our hash database since August 2007.
We are not cracking your hash in realtime - we're just caching the hard work of many cracking enthusiasts over the years.
The MD5 message-digest algorithm is a widely used hash function producing a 128-bit hash value. Although MD5 was initially designed to be used as a cryptographic hash function, it has been found to suffer from extensive vulnerabilities. It can still be used as a checksum to verify data integrity, but only against unintentional corruption. It remains suitable for other non-cryptographic purposes, for example for determining the partition for a particular key in a partitioned database. The weaknesses of MD5 have been exploited in the field, most infamously by the Flame malware in 2012. The CMU Software Engineering Institute considers MD5 essentially cryptographically broken and unsuitable for further use. MD5 Decrypt.
In cryptography, SHA-1 (Secure Hash Algorithm 1) is a cryptographic hash function which takes an input and produces a 160-bit (20-byte) hash value known as a message digest – typically rendered as a hexadecimal number, 40 digits long. It was designed by the United States National Security Agency, and is a U.S. Federal Information Processing Standard. Since 2005 SHA-1 has not been considered secure against well-funded opponents, and since 2010 many organizations have recommended its replacement by SHA-2 or SHA-3. Microsoft, Google, Apple and Mozilla have all announced that their respective browsers will stop accepting SHA-1 SSL certificates by 2017. SHA1 Decrypt.
The MySQL5 hashing algorithm implements a double binary SHA-1 hashing algorithm on a users password. MySQL Decrypt.
NT (New Technology) LAN Manager (NTLM) is a suite of Microsoft security protocols that provides authentication, integrity, and confidentiality to users. NTLM is the successor to the authentication protocol in Microsoft LAN Manager (LANMAN), an older Microsoft product. The NTLM protocol suite is implemented in a Security Support Provider, which combines the LAN Manager authentication protocol, NTLMv1, NTLMv2 and NTLM2 Session protocols in a single package. Whether these protocols are used or can be used on a system is governed by Group Policy settings, for which different versions of Windows have different default settings. NTLM passwords are considered weak because they can be brute-forced very easily with modern hardware. NTLM Decrypt.
See Full List On Cracker.offensive-security.com
SHA-2 (Secure Hash Algorithm 2) is a set of cryptographic hash functions designed by the United States National Security Agency (NSA). They are built using the Merkle–Damgård structure, from a one-way compression function itself built using the Davies–Meyer structure from a (classified) specialized block cipher. SHA-2 includes significant changes from its predecessor, SHA-1. The SHA-2 family consists of six hash functions with digests (hash values) that are 224, 256, 384 or 512 bits: SHA-224, SHA-256, SHA-384, SHA-512, SHA-512/224, SHA-512/256. Sm-j400m firmware. SHA256 Decrypt.
The Preempt research team found two critical Microsoft vulnerabilities that consist of three logical flaws in NTLM, the company's proprietary authentication protocol.
These vulnerabilities allow attackers to remotely execute malicious code on any Windows machine or authenticate to any web server that supports Windows Integrated Authentication (WIA) such as Exchange or ADFS.
The research shows that all Windows versions are vulnerable.
The flaws allow attackers to bypass existing mitigations
NTLM is susceptible to relay attacks, which allows actors to capture an authentication and relay it to another server, granting them the ability to perform operations on the remote server using the authenticated user's privileges. NTLM Relay is one of the most common attack techniques used in Active Directory environments, where the attacker compromises one machine, then moves laterally to other machines by using NTLM authentication directed at the compromised server.
Microsoft previously developed several mitigations for preventing NTLM relay attacks, but Preempt researchers discovered those mitigations have the following exploitable flaws:
The Message Integrity Code (MIC) field ensures that attackers do not tamper NTLM messages. The bypass discovered by Preempt researchers allows attackers to remove the ‘MIC' protection and modify various fields in the NTLM authentication flow, such as signing negotiation.
SMB Session Signing prevents attackers from relaying NTLM authentication messages to establish SMB and DCE/RPC sessions. The bypass enables attackers to relay NTLM authentication requests to any server in the domain, including domain controllers, while establishing a signed session to perform remote code execution. If the relayed authentication is of a privileged user, this means full domain compromise.
Enhanced Protection for Authentication (EPA) prevents attackers from relaying NTLM messages to TLS sessions. The bypass allows attackers to modify NTLM messages to generate legitimate channel binding information. This allows attackers to connect to various web servers using the attacked user's privileges and perform operations such as: read the user's emails (by relaying to OWA servers) or even connect to cloud resources (by relaying to ADFS servers).
'Even though NTLM Relay is an old technique, enterprises cannot completely eliminate the use of the protocol as it will break many applications. Hence it still poses a significant risk to enterprises, especially with new vulnerabilities discovered constantly,' stated Roman Blachman, CTO, Preempt. 'Companies need to first and foremost ensure all of their Windows systems are patched and securely configured. In addition, organizations can further protect their environments by gaining network NTLM visibility. Preempt works with its customers to ensure they have this visibility and the best protection possible.'
Protection strategies
In order to protect themselves from these vulnerabilities, organizations must:
1. Patch – Make sure that workstations and servers are properly patched. However, it is important to note that patching alone is not enough, companies also need to make configuration changes in order to be fully protected.
Cached
2. Configure
CrackStation - Online Password Hash Cracking - MD5, SHA1 ..
- Enforce SMB Signing – To prevent attackers from launching simpler NTLM relay attacks, turn on SMB Signing on all machines in the network.
- Block NTLMv1 – Since NTLMv1 is considered significantly less secure; it is recommended to completely block it by setting the appropriate GPO.
- Enforce LDAP/S Signing – To prevent NTLM relay in LDAP, enforce LDAP signing and LDAPS channel binding on domain controllers.
- Enforce EPA – To prevent NTLM relay on web servers, harden all web servers (OWA, ADFS) to accept only requests with EPA.
3. Reduce NTLM usage – Even with fully secured configuration and patched servers, NTLM poses a significantly greater risk than Kerberos. It is recommended that you remove NTLM where it is not needed.
What Are Hash Files? (with Picture) - WiseGEEK
As of June 11, 2019, Microsoft has issued CVE-2019-1040 and CVE-2019-1019 on Patch Tuesday per Preempt's responsible disclosure of the NTLM vulnerabilities.
